Quilts Production Line
Description
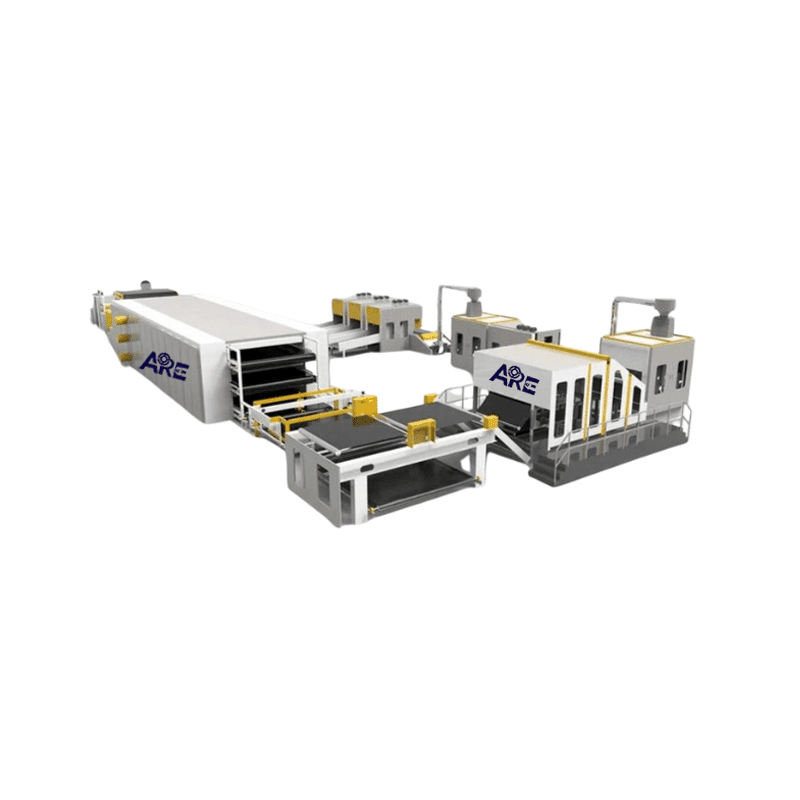
Quilts Production Line (wadding production line )

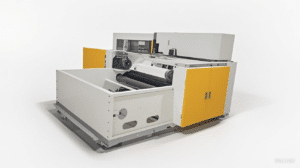
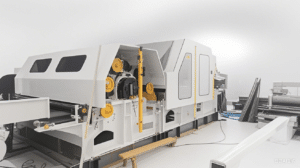

A wadding production line refers to a manufacturing line for fluffy materials (such as cotton, chemical fibers, etc.), mainly used to process raw materials into filling materials suitable for products like quilts and clothing.
The following introduces it from aspects such as production processes, equipment, and application scenarios:
Core Production Processes
1. Raw Material Processing
Open up raw materials like cotton, chemical fibers (e.g., polyester), and wool through a carding machine to break up clumps, making them fluffy and uniform.
If using mixed materials, proportionally blend them (e.g., cotton and chemical fiber blends) to ensure even filling.
2. Combing and Web Laying
Use a combing machine to comb the opened fibers into thin webs, removing impurities and short fibers to make the fibers more orderly.
Stack multiple thin webs into a fiber layer (i.e., “cotton wadding” or “chemical fiber floc”) with a certain thickness.
3. Shaping and Reinforcement
◦ Fix the fiber layer into shape through processes like needling, hot-melting (heating and melting chemical fibers for adhesion), or chemical bonding (adding adhesives) to prevent displacement or clumping during use.
◦ Some production lines add functional treatments like antibacterial and anti-mite processes (e.g., spraying antibacterial agents).
4. Cutting and Quality Inspection
◦ Cut the floc according to specifications and check indicators such as thickness, fluffiness, and impurity content to ensure they meet the filling requirements for subsequent products (e.g., quilts, pillows).
Key Production Equipment
• Carding Machine: Breaks up raw material clumps, commonly used in cotton and wool processing.
• Combing Machine: Combs fibers and forms uniform webs, including doffer combing machines and roller combing machines.
• Needling Machine: Penetrates the fiber layer with needles to interlock and shape it, mostly for chemical fibers or mixed materials.
• Hot-Melt Shaping Machine: Heats chemical fiber flocs to bond them using fiber melting points, suitable for industrial mass production.
Application Scenarios
• Home Textiles: Produces fillings for quilts, pillows, and mattresses (e.g., cotton wadding cores, chemical fiber wadding cores).
• Garment Industry: Used for filling cotton in down jackets and cold-proof clothing (e.g., silk-like cotton, spray-bonded cotton).
• Other Fields: Production of filling wadding for sofas, toys, soundproof materials, etc.
Typical Technologies and Brands
• Glue-Free Cotton Technology: Uses hot-melting to self-bond chemical fiber flocs, avoiding chemical adhesives for greater environmental friendliness (e.g., in some baby home textile products).
• Antibacterial and Anti-Mite Treatment: Adds nano-level antibacterial agents during production to enhance the hygienic performance of wadding (common in high-end home textile brands).
In short, the wadding production line processes fiber raw materials into fluffy and uniform filling materials through mechanized processes, serving as a key link in the home textile and clothing industry chains.